“A new model approach for reactive solute transport in dual-permeability media with depth-dependent reaction coefficients” was published in Journal of Hydrogeology (Volume 577, October 2019, 123946). It is an achievement of Prof. WEN Zhang’s team from the School of Environmental Studies. The first author is second-year doctoral student XIE Shuang, and WEN is the corresponding author.
In this study, we developed a one-dimensional mobile-mobile model (MM) for contaminant transport in subsurface with depth-dependent reaction coefficients. Two local systems at micro-scale level are involved in this model: a micro-pore system and a less permeable pore system. The breakthrough curves (BTCs) obtained from the MM with depth-dependent coefficients were thoroughly analyzed, where the case with constant coefficients was used as the reference system. The effects of different parameters on BTCs were studied, and a parameter analysis was also performed to illustrate the effects of adsorption coefficient and degradation coefficient on BTCs. Results show that the BTC patterns for the depth-dependent reactions, in which the reaction rate decreases with increasing depth, vary between the two extreme cases with constant-rate reactions in the topsoil and observation depth. The mass transfer coefficient (α) plays a significant role in defining the BTC pattern. The double peak changes to a single peak when the value of α is large enough. In addition, the velocity of the main flow determines the shape of the BTCs while the velocity of the SVD defines the pattern of the dual peaks in BTCs which also tends to be represented by a single peak as the velocity decreases. Finally, we tested the applicability of the proposed model (MM-FD) in the leaching experiments of both field herbicide and conservative tracer in an agricultural area of northeastern Greece, and compared its performance with that of the advection-dispersion equation (ADE) model by Gao et al. (2013), both of which have depth-dependent coefficients. The results showed that the proposed mobile-mobile model with depth-dependent reaction coefficients was able to satisfactorily capture the evolution of metolachlor concentration both at upper and lower depths.
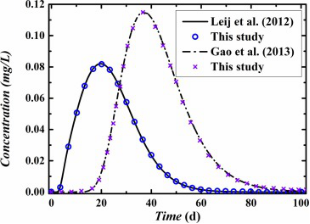
Fig. 1. Comparison of the analytical (semi-analytical) and numerical solutions.
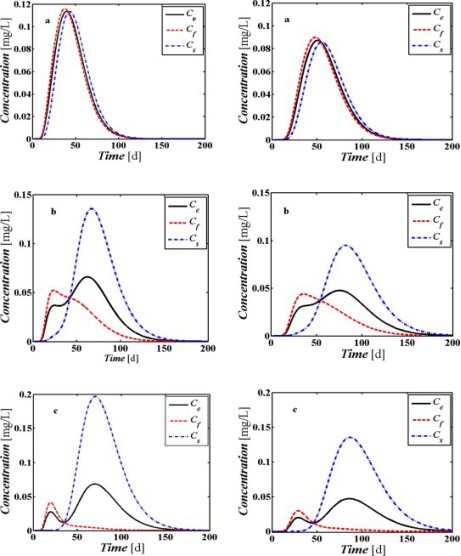
Fig. 2. BTCs for Cf and Cs and average flux concentration at 60 cm with (a) α = 0.05 (b) α = 0.005 (c) α = 0.0005 for (left) x0 = 30 cm and (right) x0 = 60 cm.
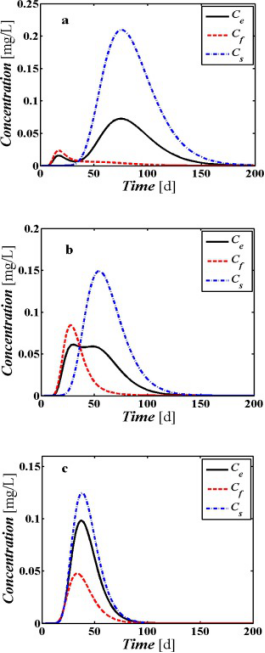
Fig. 3. BTCs for Cs and Cf and the average flux concentration Ce at 60 cm with (a) vf = 20 cm/d, θf = 0.05 (qf = 1 cm/d) and vs = 1.11 cm/d, θs = 0.45 (qs = 0.5 cm/d) (b) vf = 4 cm/d, θf = 0.25 (qf = 1 cm/d) and vs = 2 cm/d, θs = 0.25 (qs = 0.5 cm/d) (c) vf = 10 cm/d, θf = 0.05 (qf = 0.5 cm/d) and vs = 2.22 cm/d, θs = 0.45 (qs = 1 cm/d).
Full Text: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.123946 or
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169419306663